New Analysis: Technoeconomics (TECH) report– EPDM Rubber
EPDM is a relatively new rubber commercially developed in the early 1960s, compared to SBR (styrene-butadiene rubber) or NBR (acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber), which were the first synthetic rubbers that were developed in the late 1930s. Unlike SBR, which was developed as an inexpensive replacement for natural rubber in tires, EPDM is primarily used in non-tire applications because of its higher performance and cost. EPDM has a fully saturated molecular backbone that provides excellent ozone resistance, weatherability and heat resistance properties, very good dielectric performance, and low temperature flexibility.
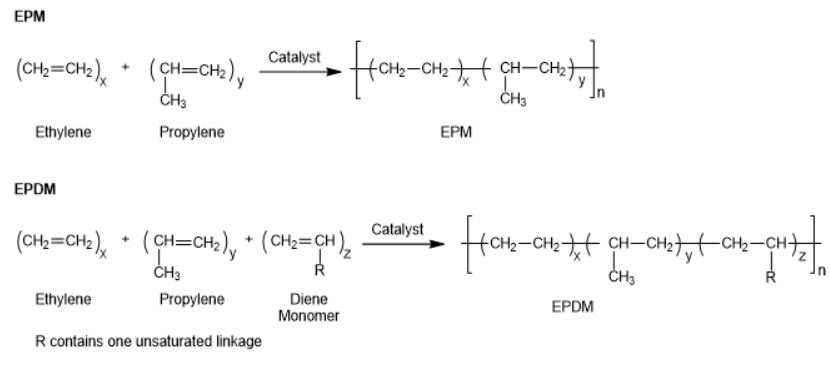
EPDM can be produced either as an ethylene/propylene copolymer (EPM) or as a terpolymer of ethylene, propylene, and another moiety containing side-chain unsaturation such as ethylidene-5-norbornene-2 (ENB).
NexantECA EPDM rubber
The advantage of side-chain unsaturation is that the resulting polymer can be sulfur cured, as is performed with other rubbers.
Commercial Technologies
EPDM is produced in a solution reactor based on Ziegler-Natta or Metallocene-catalyzed chemistry, or in a Ziegler-Natta catalyzed slurry process. Metallocene or other single site catalysts have altered the industry, as such catalysts permit new and different molecular architectures at lower cost. The lower cost is a result of increased catalyst activity and less residual process waste.
Process Economics
For this report, NexantECA evaluated the three main processes available for EPDM production – Ziegler-Natta solution, Metallocene solution, and Ziegler-Natta slurry processes. The evaluation provides:
Process description with simplified flow sheets
Recent developments related to process technology
Investment and cost of production (COP) estimates for a grassroots facility
Estimates are made for plants located in the USGC, Western Europe, and the China Coast
Commercial Overview
Key end-use markets, applications and market trends are developed for EPDM for the regions – North America, Western Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of World. Demand and supply/demand balances are provided for 2011 to 2026.
The COVID-induced recession, which followed a period of numerous capacity additions, resulted in poor operating rates and a shut-down of a number of plants, as discussed in the report. A listing of producers is provided.
EPDM rubbers report NexantECA
Subscribe to TECH
The TECH program (formerly known as PERP) is globally recognized as the industry standard source of process evaluations of existing, new and emerging of interest to the energy and chemical industries.
TECH’s comprehensive studies include detailed technology analyses, process economics, as well as commercial overviews and industry trends. Reports typically cover:
Trends in chemical technology
Strategic/business overviews
Process Technology:
Chemistry
Process flow diagrams and descriptions of established/conventional, new and emerging processes
Process economics – comparative costs of production estimates for different technologies across various geographic regions
Overview of product applications and markets for new as well as established products
Regional supply and demand balances for product, including capacity tables of plants in each region
Regulatory and environmental issues where relevant
Subscription Options
A subscription to TECH comprises:
PDF reports including detailed technology analyses, process economics, as well as commercial overviews and industry trends
Cost of production tables in spreadsheet format
Consultation time with the project team
An annual subscription to TECH includes twenty reports published in a given program year. Reports can also be purchased on an individual basis, including reports from previous program years.